What Are Tooth Implants Made Of? Discover the Best Materials
Tooth implants are primarily made from titanium and zirconia, both chosen for their strength and biocompatibility. In this article, we will explore what are tooth implants made of, including these materials and others used in dental implants, along with their specific roles and benefits.
Key Takeaways
- Dental implants consist of three main components: the implant post, abutment, and restoration, each playing a vital role in creating a stable and natural-looking tooth replacement.
- Materials used for implant posts, specifically titanium and zirconia, offer distinct advantages; titanium is known for its durability and osseointegration, while zirconia provides aesthetic benefits for patients with metal allergies.
- Choosing the right dental implant material should consider individual factors such as budget, dental health, and aesthetic goals, and it is essential to consult with a dentist to make an informed decision.
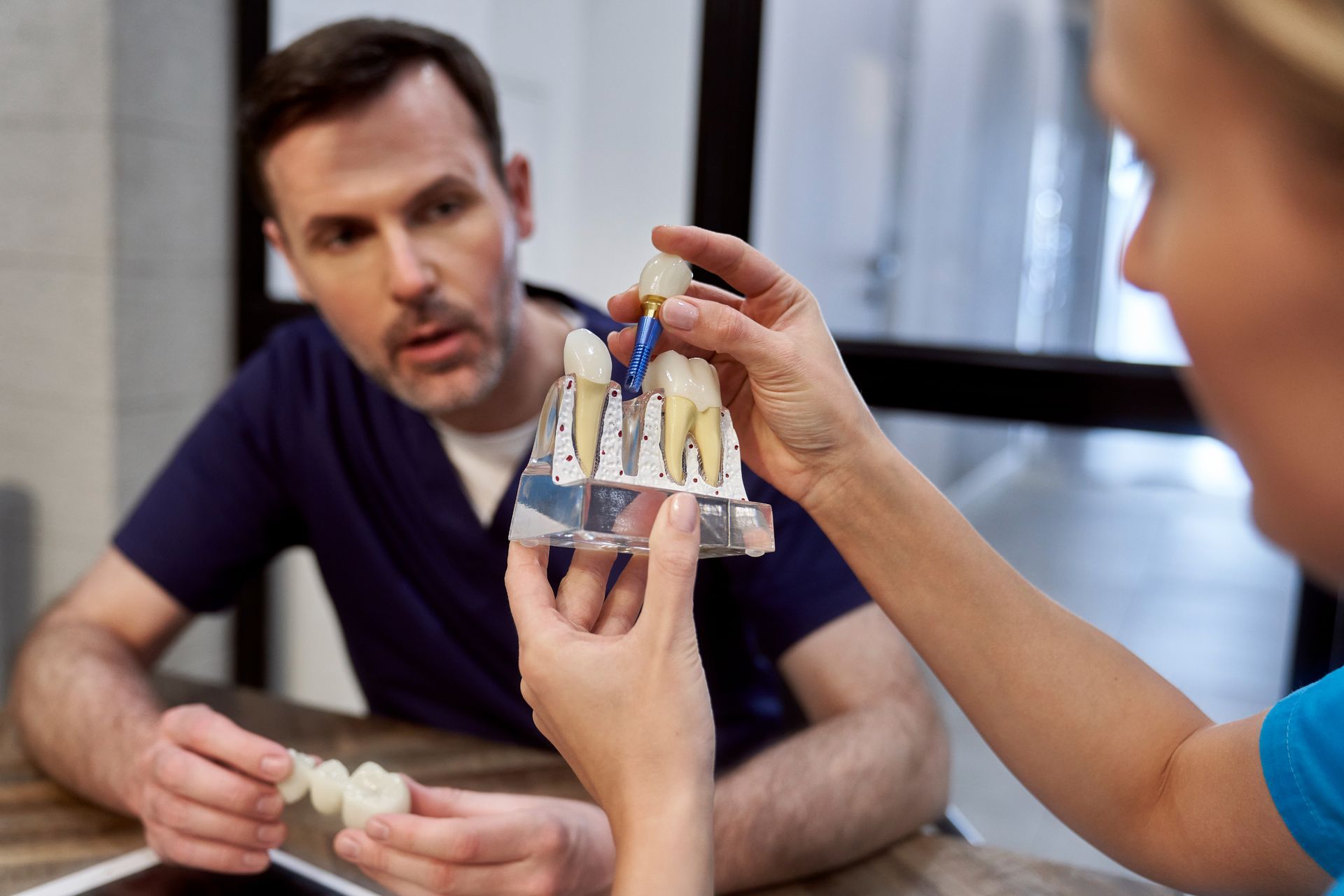
Components of Tooth Implants
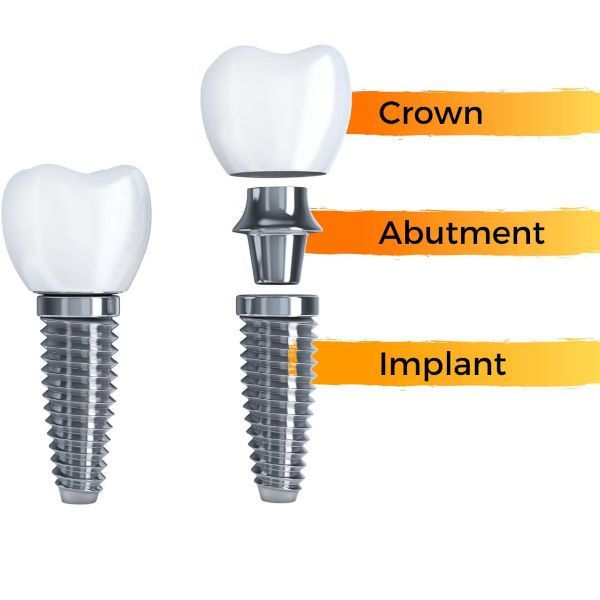
Dental implants consist of three main components: the implant post, the abutment, and the restoration.
Each one ensures a stable and natural-looking tooth replacement.
The implant post, surgically inserted into the jawbone, undergoes osseointegration, bonding with the bone to create a stable foundation for the rest of the implant. This process is crucial for the implant’s longevity and effectiveness.
The abutment, a small connector, links the implant post to the restoration, ensuring it fits properly and sits securely.
The restoration, the visible portion of the implant, mimics natural teeth in color, shape, and size, providing an aesthetically pleasing and seamless smile.
Common Materials Used for Implant Posts
The materials for implant posts, such as titanium alloys and zirconia, are crucial for durability and biocompatibility.
Titanium’s biocompatibility, non-allergenic properties, and ability to bond with the jawbone through osseointegration make it a popular choice. Its strength and durability are especially beneficial for high-chewing areas.
Zirconia, a metal-free alternative to titanium, is less rigid, facilitating easier abutment attachment. It is suitable for patients with metal allergies. The choice between these materials depends on individual needs and preferences.
Abutment Materials: Connecting the Implant to Restoration
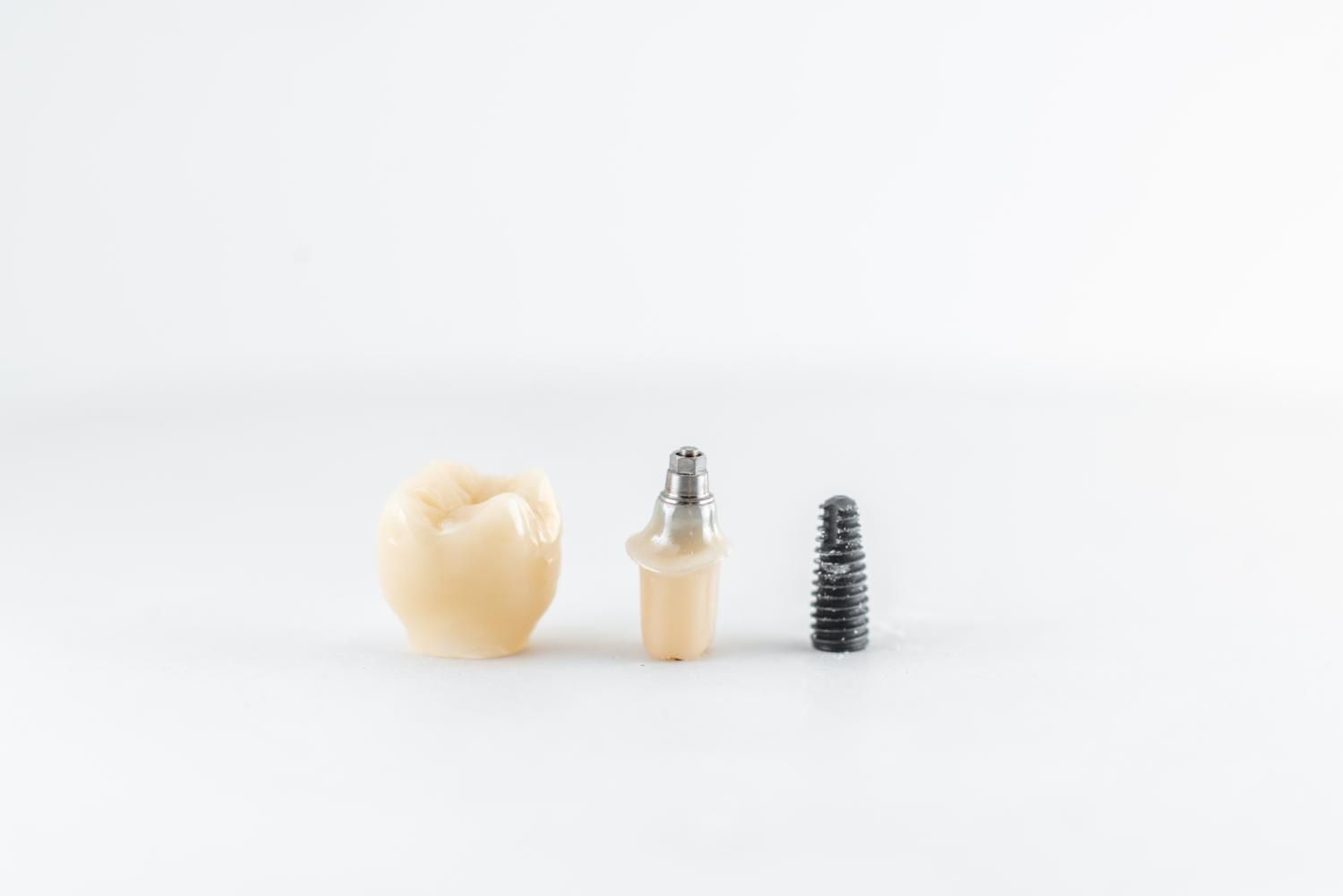
Common abutment materials, such as titanium and zirconia, connect the implant post to the restoration, each with its own advantages.
Titanium abutments, known for their compatibility with biological tissues, provide a stable and durable connection between the implant post and restoration, ensuring long-term success.
Zirconia abutments offer high mechanical strength and aesthetic benefits, with lower surface energy that reduces plaque accumulation and promotes better peri-implant health.
Restoration Materials: Creating Natural-Looking Teeth
The restoration, the visible part of the implant, requires materials like porcelain, ceramic, and zirconia for a natural-looking result.
Porcelain, popular for its aesthetic qualities, can be custom-made to match the color and translucency of natural teeth, providing a lifelike and durable restoration.
Zirconia restorations, known for their tooth-like appearance and minimal gum irritation, provide strength and durability, making them a preferred choice for many.
Ceramics, including carbon silicon, are used for their strength and compatibility with natural teeth, offering a pleasing appearance despite some brittleness.
Comparing Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants
When choosing between titanium and zirconia implants, consider their strengths and weaknesses. Titanium’s proven success in osseointegration and flexibility enhances implant longevity, though its metallic appearance may be less aesthetic.
Zirconia implants offer aesthetic advantages with their tooth-like color but can be more susceptible to cracking under heavy pressure, limiting their use in high-stress areas.
Ultimately, the choice between titanium and zirconia hinges on individual needs and preferences, with each material offering unique benefits.
Alternative Materials for Tooth Implants
Besides titanium and zirconia, alternative materials like polymethacrylate, carbon-silicon, stainless steel, gold, and cobalt-chromium are used in dental implants, each with unique properties.
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is an innovative, tough, durable, and naturally colored material. Its biocompatibility makes it suitable for patients with metal allergies.
Cobalt-chromium, known for its strength and durability, is a viable but less common option compared to titanium or zirconia, providing alternative metals unlike titanium for specific patient needs.
Safety and Biocompatibility of Dental Implant Materials
Safety and biocompatibility are crucial when choosing dental implant materials. Testing ensures that implant materials do not provoke adverse reactions in the body.
The FDA oversees the safety of dental implant materials, regulating their use. Tests like fatigue, shear, tension, and bending fatigue evaluate performance and durability.
Research shows that titanium alloys in dental implants do not negatively affect the body, despite minor amounts entering the bloodstream. Testing ensures long-term safety and effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Dental Implant
Choosing the right dental implant material involves factors like budget, age, dental health, and teeth grinding. Selecting a material that meets your specific needs and preferences is crucial.
A dental consultation is necessary for making an informed decision. During the consultation, patients can discuss various treatment options and receive tailored advice based on their oral health status and aesthetic goals. The consultation process often includes a comprehensive review of the patient’s dental history and treatment requirements.
Cost is an important factor when selecting implant materials. Zirconia implants usually cost more, and insurance coverage may vary. Discussing these factors with your dentist can help in making the best decision.
The Role of Implant Dentistry in Oral Health
Dental implants play a vital role in maintaining oral health. Dental implants stimulate the jawbone, preventing bone loss and maintaining facial structure. This stimulation helps preserve the jawbone’s density, which is crucial for long-term oral health.
Implants promote better oral hygiene by reducing gum disease risk. Unlike dentures, they do not irritate gums, lowering inflammation and infection, and contributing to better immune health.
Dental implants allow full bite force, improving diet variety and nutrition. They also help maintain bite alignment, reducing uneven wear and associated dental issues.
Schedule a Consultation with Our Dentists
Choosing the right dental implant provider is crucial for a successful outcome. Consider the provider’s experience, accreditation, and patient-centered approach. Scheduling a consultation with our dentists helps discuss specific needs and learn about the best options.
During the consultation, patients should share their health concerns and preferences to receive tailored advice on how to create dental implants. We encourage scheduling a consultation to start the journey to improved oral health.
Summary
In summary, understanding the materials used in dental implants is crucial for making an informed decision about your dental health. From the components of dental implants to the various materials used for implant posts, abutments, and restorations, each element plays a vital role in the success and longevity of the implant.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the world of dental implants. If you’re considering dental implants, we encourage you to consult with a qualified dentist to explore your options and find the best solution for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Orlando Lifestyle Dentistry
What are the main components of a dental implant?
The main components of a dental implant are the implant post, abutment, and restoration. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring the implant's stability and functionality.
What materials are commonly used for dental implant posts?
Dental implant posts are most commonly made from titanium alloys and zirconia. These materials provide strength and biocompatibility, essential for successful implantation.
How do I choose the right material for my dental implant?
To choose the right material for your dental implant, evaluate your budget, health condition, and aesthetic preferences, and seek guidance from a qualified dentist. This approach will ensure the best outcome for your specific needs.
What are the benefits of titanium vs. zirconia implants?
Titanium implants are known for their strength and durability, making them highly reliable, while zirconia implants offer aesthetic advantages and are metal-free, appealing to those seeking a non-metal option. Both materials have distinct benefits depending on patient needs.
How do dental implants improve oral health?
Dental implants significantly enhance oral health by stimulating the jawbone, preventing bone loss, and reducing the risk of gum disease. They also improve bite force and alignment.